Configure a WPA2 Enterprise WLAN on the WLC
Summary
This topic configure a WLC WLAN to use a VLAN interface, a DHCP server, and WPA2 Enterprise authentication. Start learning CCNA 200-301 for free right now!!
Table of Contents
Video – Define an SNMP and RADIUS Server on the WLC
The previous topic covered configuring a basic WLAN on the WLC. Now you will learn about configuring a WPA2 Enterprise WLAN.
Click Play in the figure to view a demonstration of configuring SNMP and RADIUS services on the WLC.
SNMP and RADIUS
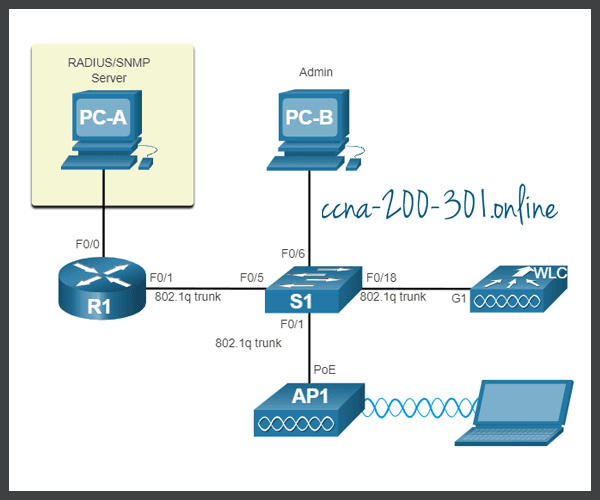
In the figure, PC-A is running Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) server software. SNMP is used to monitor the network. The network administrator wants the WLC to forward all SNMP log messages, called traps, to the SNMP server.
In addition, for WLAN user authentication, the network administrator wants to use a RADIUS server for authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) services. Instead of entering a publicly known pre-shared key to authenticate, as they do with WPA2-PSK, users will enter their own username and password credentials. The credentials will be verified by the RADIUS server. This way, individual user access can be tracked and audited if necessary and user accounts can be added or modified from a central location. The RADIUS server is required for WLANs that are using WPA2 Enterprise authentication.
The figure depicts a network topology. PC-A is a RADIUS/SNMP Server connected to R1 on R1s F0/0 interface. PC-B is connected to S1 on S1s F0/6 port. R1 and S1 are connected together on R1s F0/1 interface and on S1s F0/5 interface. S1 is connected to a WLC on its F0/18 port. On S1s F0/1 port its connected to an access point, AP1. A laptop is wirelessly connected to AP1.
Topology
Configure SNMP Server Information
Click the MANAGEMENT tab to access a variety of management features. SNMP is listed at the top of the menu on the left. Click SNMP to expand the sub-menus, and then click Trap Receivers. Click New… to configure a new SNMP trap receiver, as shown in the figure.
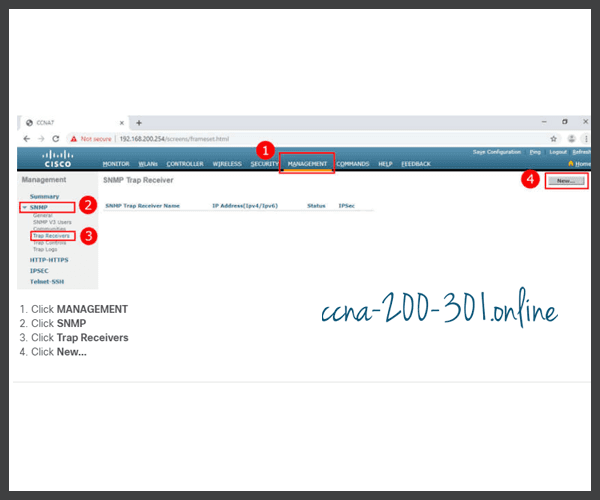
Enter the SNMP Community name and the IP address (IPv4 or IPv6) for the SNMP server. Click Apply. The WLC will now forward SNMP log messages to the SNMP server.

Configure RADIUS Server Information
In our example configuration, the network administrator wants to configure a WLAN using WPA2 Enterprise, as opposed to WPA2 Personal or WPA2 PSK. Authentication will be handled by the RADIUS server running on PC-A.
To configure the WLC with the RADIUS server information, click the SECURITY tab > RADIUS > Authentication. No RADIUS servers are currently configured. Click New… to add PC-A as the RADIUS server.
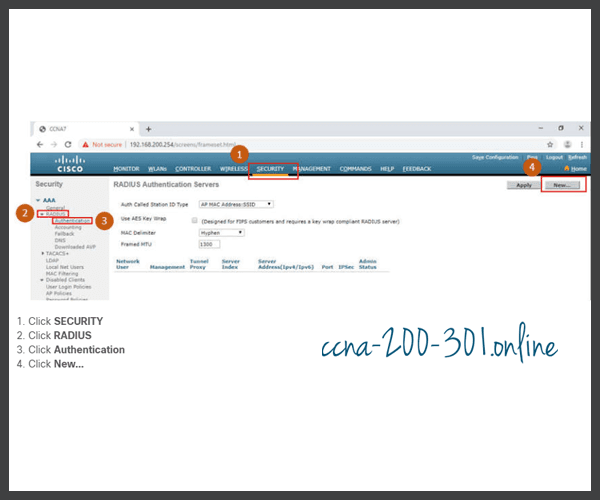
Enter the IPv4 address for PC-A and the shared secret. This is the password used between the WLC and the RADIUS server. It is not for users. Click Apply, as shown in the figure.

After clicking Apply, the list of configured RADIUS Authentication Servers refreshes with the new server listed, as shown in the figure.

Video – Configure a VLAN for a New WLAN
Click Play in the figure to view a demonstration of configuring a VLAN on the WLC.
Topology with VLAN 5 Addressing
Each WLAN configured on the WLC needs its own virtual interface. The WLC has five physical ports for data traffic. Each physical port can be configured to support multiple WLANs, each on its own virtual interface. Physical ports can also be aggregated to create high-bandwidth links.
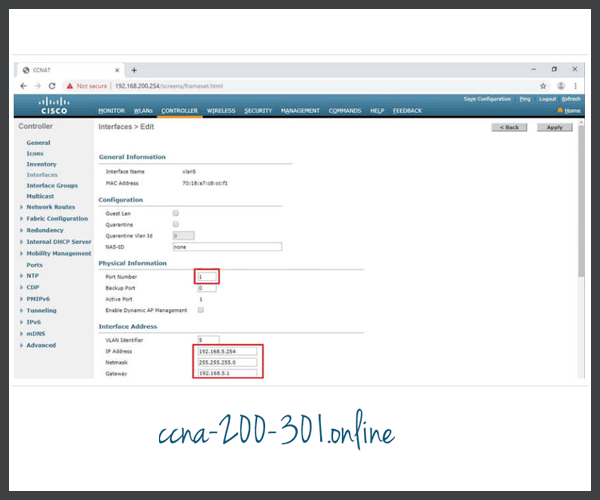
The network administrator has decided that the new WLAN will use interface VLAN 5 and network 192.168.5.0/24. R1 already has a subinterface configured and active for VLAN 5, as shown in the topology and show ip interface brief output.
Topology

R1# show ip interface brief Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol FastEthernet0/0 172.16.1.1 YES manual up up FastEthernet0/1 unassigned YES unset up up FastEthernet0/1.1 192.168.200.1 YES manual up up FastEthernet0/1.5 192.168.5.254 YES manual up up (output omitted) R1#
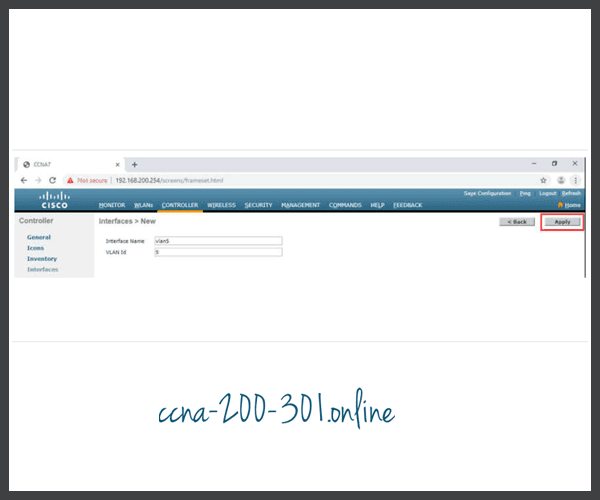
Configure a New Interface
VLAN interface configuration on the WLC includes the following steps:
- Create a new interface.
- Configure the VLAN name and ID.
- Configure the port and interface address.
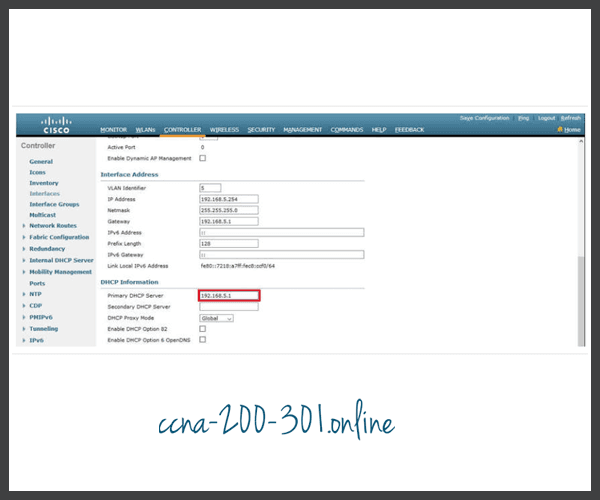
- Configure the DHCP server address.
- Apply and Confirm.
- Verify Interfaces.
Click each step for more information and an example GUI.
Video – Configure a DHCP Scope
Click Play in the figure to view a demonstration of configuring DHCP services.
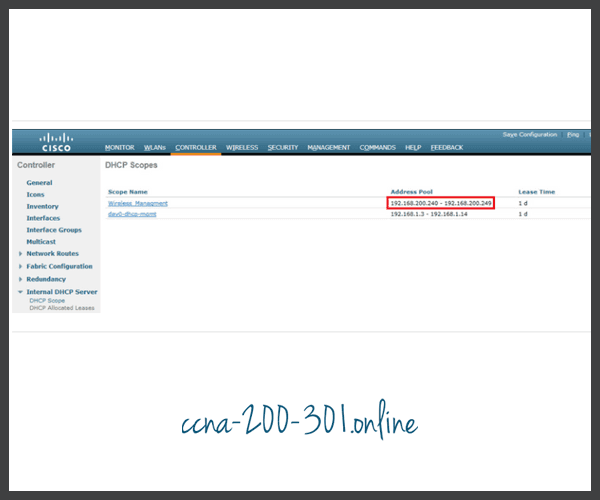
Configure a DHCP Scope
DHCP scope configuration includes the following steps:
- Create a new DHCP scope.
- Name the DHCP scope.
- Verify the new DHCP scope.
- Configure and enable the new DHCP scope.
- Verify the enable DHCP scope
Click each step for more information and an example GUI.
Video – Configure a WPA2 Enterprise WLAN
Click Play in the figure to view a demonstration of configuring a new WLAN with WPA2 Enterprise on the WLC.
Configure a WPA2 Enterprise WLAN
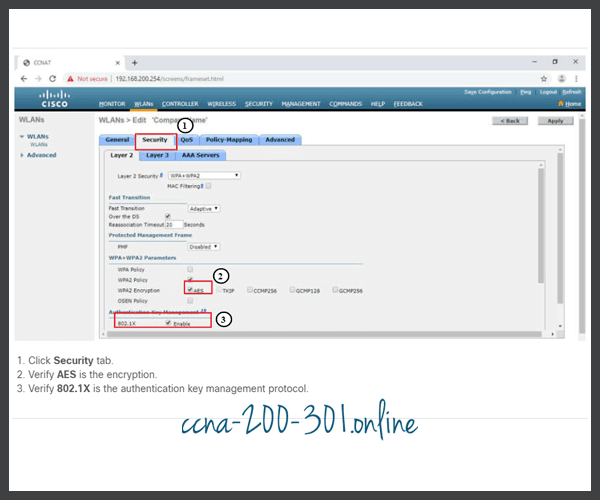
By default, all newly created WLANs on the WLC will use WPA2 with Advanced Encryption System (AES). 802.1X is the default key management protocol used to communicate with the RADIUS server. Because the network administrator already configured the WLC with the IPv4 address of the RADIUS server running on PC-A, the only configuration left to do is to create a new WLAN to use interface vlan5.
Configuring a new WLAN on the WLC includes the following steps:
- Create a new WLAN.
- Configure the WLAN name and SSID.
- Enable the WLAN for VLAN 5.
- Verify AES and 802.1X defaults.
- Configure WLAN security to use the RADIUS server.
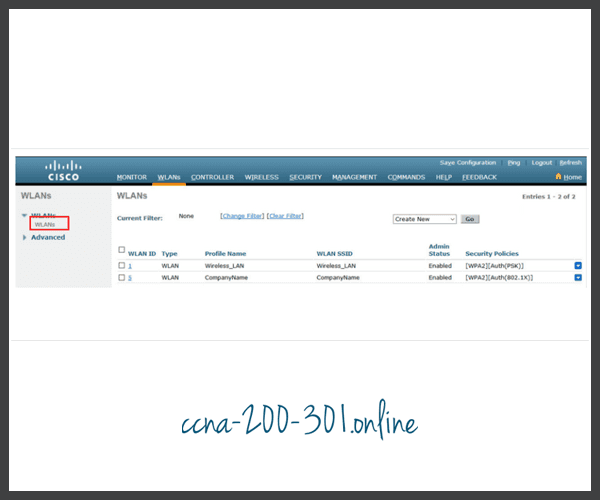
- Verify the new WLAN is available.
Click each step for more information and an example GUI.
Packet Tracer – Configure a WPA2 Enterprise WLAN on the WLC
In this activity, you will configure a new WLAN on a wireless LAN controller (WLC), including the VLAN interface that it will use. You will configure the WLAN to use a RADIUS server and WPA2-Enterprise to authenticate users. You will also configure the WLC to use an SNMP server.
Ready to go! Keep visiting our networking course blog, give Like to our fanpage; and you will find more tools and concepts that will make you a networking professional.