CAPWAP Operation
Summary
This topic explain how a WLC uses CAPWAP to manage multiple APs. Start learning CCNA 200-301 for free right now!!
Table of Contents
Video – CAPWAP
In the previous topic you learned about WLAN operation. Now you will learn about Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP).
Click Play to view a video about Control and Provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP) protocol.
Introduction to CAPWAP
CAPWAP is an IEEE standard protocol that enables a WLC to manage multiple APs and WLANs. CAPWAP is also responsible for the encapsulation and forwarding of WLAN client traffic between an AP and a WLC.
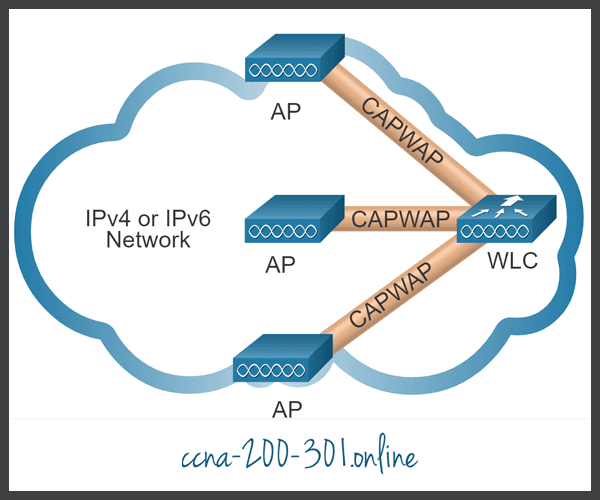
CAPWAP is based on LWAPP but adds additional security with Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS). CAPWAP establishes tunnels on User Datagram Protocol (UDP) ports. CAPWAP can operate either over IPv4 or IPv6, as shown in the figure, but uses IPv4 by default.
IPv4 and IPv6 can use UDP ports 5246 and 5247. However, CAPWAP tunnels use different IP protocols in the frame header. IPv4 uses IP protocol 17 and IPv6 uses IP protocol 136.
Split MAC Architecture
A key component of CAPWAP is the concept of a split media access control (MAC). The CAPWAP split MAC concept does all of the functions normally performed by individual APs and distributes them between two functional components:
- AP MAC Functions
- WLC MAC Functions
The table shows some of the MAC functions performed by each
| AP MAC Functions | WLC MAC Functions |
|---|---|
| Beacons and probe responses | Authentication |
| Packet acknowledgements and retransmissions | Association and re-association of roaming clients |
| Frame queueing and packet prioritization | Frame translation to other protocols |
| MAC layer data encryption and decryption | Termination of 802.11 traffic on a wired interface |
DTLS Encryption
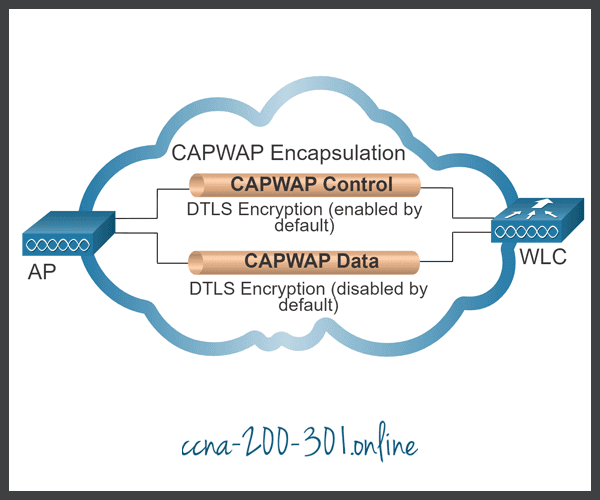
DTLS is a protocol which provides security between the AP and the WLC. It allows them to communicate using encryption and prevents eavesdropping or tampering.
DTLS is enabled by default to secure the CAPWAP control channel but is disabled by default for the data channel, as shown in the figure. All CAPWAP management and control traffic exchanged between an AP and WLC is encrypted and secured by default to provide control plane privacy and prevent Man-In-the-Middle (MITM) attacks.
CAPWAP data encryption is optional and is enabled per AP. Data encryption requires a DTLS license to be installed on the WLC prior to being enabled on an AP. When enabled, all WLAN client traffic is encrypted at the AP before being forwarded to the WLC and vice versa.
FlexConnect APs
FlexConnect is a wireless solution for branch office and remote office deployments. It lets you configure and control access points in a branch office from the corporate office through a WAN link, without deploying a controller in each office.
There are two modes of operation for the FlexConnect AP.
- Connected mode – The WLC is reachable. In this mode the FlexConnect AP has CAPWAP connectivity with its WLC and can send traffic through the CAPWAP tunnel, as shown in the figure. The WLC performs all its CAPWAP functions.
- Standalone mode – The WLC is unreachable. The FlexConnect has lost or failed to establish CAPWAP connectivity with its WLC. In this mode, a FlexConnect AP can assume some of the WLC functions such as switching client data traffic locally and performing client authentication locally.

Ready to go! Keep visiting our networking course blog, give Like to our fanpage; and you will find more tools and concepts that will make you a networking professional.





