OSPF Router ID
Summary
This topic configure an OSPFv2 router ID.. Start learning CCNA 200-301 for free right now!!
Table of Contents
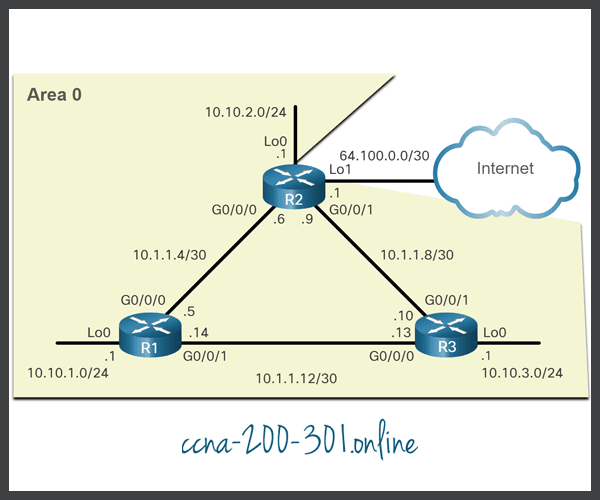
OSPF Reference Topology
To get you started, this topic discusses the foundation on which OSPF bases its entire process, the OSPF router ID.
The figure shows the topology used for configuring OSPFv2 in this module. The routers in the topology have a starting configuration, including interface addresses. There is currently no static routing or dynamic routing configured on any of the routers. All interfaces on R1, R2, and R3 (except the loopback 1 on R2) are within the OSPF backbone area. The ISP router is used as the gateway to the internet of the routing domain.
Router Configuration Mode for OSPF
OSPFv2 is enabled using the router ospf process-id global configuration mode command, as shown in the command window for R1. The process-id value represents a number between 1 and 65,535 and is selected by the network administrator. The process-id value is locally significant, which means that it does not have to be the same value on the other OSPF routers to establish adjacencies with those neighbors. It is considered best practice to use the same process-id on all OSPF routers.
After entering the router ospf process-id command, the router enters router configuration mode, as indicated by the R1(config-router)# prompt. Enter a question mark (?), to view all the commands available in this mode. The list of commands shown here has been altered to display only the commands that are relevant to this module.
R1(config)# router ospf 10 R1(config-router)# ? area OSPF area parameters auto-cost Calculate OSPF interface cost according to bandwidth default-information Control distribution of default information distance Define an administrative distance exit Exit from routing protocol configuration mode log-adjacency-changes Log changes in adjacency state neighbor Specify a neighbor router network Enable routing on an IP network no Negate a command or set its defaults passive-interface Suppress routing updates on an interface redistribute Redistribute information from another routing protocol router-id router-id for this OSPF process R1(config-router)#
Router IDs
An OSPF router ID is a 32-bit value, represented as an IPv4 address. The router ID is used to uniquely identify an OSPF router. All OSPF packets include the router ID of the originating router. Every router requires a router ID to participate in an OSPF domain. The router ID can be defined by an administrator or automatically assigned by the router. The router ID is used by an OSPF-enabled router to do the following:
- Participate in the synchronization of OSPF databases – During the Exchange State, the router with the highest router ID will send their database descriptor (DBD) packets first.
- Participate in the election of the designated router (DR) – In a multiaccess LAN environment, the router with the highest router ID is elected the DR. The routing device with the second highest router ID is elected the backup designated router (BDR).
Router ID Order of Precedence
But how does the router determine the router ID? As illustrated in the figure, Cisco routers derive the router ID based on one of three criteria, in the following preferential order:
- The router ID is explicitly configured using the OSPF router-id rid router configuration mode command. The rid value is any 32-bit value expressed as an IPv4 address. This is the recommended method to assign a router ID.
- If the router ID is not explicitly configured, the router chooses the highest IPv4 address of any of configured loopback interfaces. This is the next best alternative to assigning a router ID.
- If no loopback interfaces are configured, then the router chooses the highest active IPv4 address of any of its physical interfaces. This is the least recommended method because it makes it more difficult for administrators to distinguish between specific routers.

Configure a Loopback Interface as the Router ID
In the reference topology, only the physical interfaces are configured and active. The loopback interfaces have not been configured. When OSPF routing is enabled on the router, the routers would pick the following highest active configured IPv4 address as the router ID.
- R1: 10.1.1.14 (G0/0/1)
- R2: 10.1.1.9 (G0/0/1)
- R3: 10.1.1.13 (G0/0/0)
Instead of relying on physical interface, the router ID can be assigned to a loopback interface. Typically, the IPv4 address for this type of loopback interface should be configured using a 32-bit subnet mask (255.255.255.255). This effectively creates a host route. A 32-bit host route would not get advertised as a route to other OSPF routers.
The example shows how to configure a loopback interface on R1. Assuming the router ID was not explicitly configured or previously learned, R1 will use IPv4 address 1.1.1.1 as its router ID. Assume R1 has not yet learned a router ID.
R1(config-if)# interface Loopback 1 R1(config-if)# ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 R1(config-if)# end R1# show ip protocols | include Router ID Router ID 1.1.1.1 R1#
Explicitly Configure a Router ID
In the figure, the topology has been updated to show the router ID for each router:
- R1 uses router ID 1.1.1.1
- R2 uses router ID 2.2.2.2
- R3 uses router ID 3.3.3.3

Use the router-id rid router configuration mode command to manually assign a router ID. In the example, the router ID 1.1.1.1 is assigned to R1. Use the show ip protocols command to verify the router ID.
R1(config)# router ospf 10
R1(config-router)# router-id 1.1.1.1
R1(config-router)# end
*May 23 19:33:42.689: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
R1# show ip protocols | include Router ID
Router ID 1.1.1.1
R1#
Modify a Router ID
After a router selects a router ID, an active OSPF router does not allow the router ID to be changed until the router is reloaded or the OSPF process is reset.
In example for R1, the configured router ID has been removed and the router reloaded. Notice that the current router ID is 10.10.1.1, which is the Loopback 0 IPv4 address. The router ID should be 1.1.1.1. Therefore, R1 is configured with the command router-id 1.1.1.1.
Notice how an informational message appears stating that the OSPF process must be cleared or that the router must be reloaded. The reason is because R1 already has adjacencies with other neighbors using the router ID 10.10.1.1. Those adjacencies must be renegotiated using the new router ID 1.1.1.1. Use the clear ip ospf process command to reset the adjacencies. You can then verify that R1 is using the new router ID command with the show ip protocols command piped to display only the router ID section.
Clearing the OSPF process is the preferred method to reset the router ID.
R1# show ip protocols | include Router ID Router ID 10.10.1.1 R1# conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R1(config)# router ospf 10 R1(config-router)# router-id 1.1.1.1 % OSPF: Reload or use "clear ip ospf process" command, for this to take effect R1(config-router)# end R1# clear ip ospf process Reset ALL OSPF processes? [no]: y *Jun 6 01:09:46.975: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 10, Nbr 3.3.3.3 on GigabitEthernet0/0/1 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached *Jun 6 01:09:46.975: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 10, Nbr 2.2.2.2 on GigabitEthernet0/0/0 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached *Jun 6 01:09:46.981: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 10, Nbr 3.3.3.3 on GigabitEthernet0/0/1 from LOADING to FULL, Loading Done *Jun 6 01:09:46.981: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 10, Nbr 2.2.2.2 on GigabitEthernet0/0/0 from LOADING to FULL, Loading Done R1# show ip protocols | include Router ID Router ID 1.1.1.1 R1#
Syntax Checker – Configure R2 and R3 Router IDs
Use the Syntax Checker to configure R2 and R3 with router IDs.
You are currently logged into R2:
- Enter OSPF router configuration mode using process ID 10
- Assign a router ID of 2.2.2.2
- Return to privileged EXEC mode
R2(config)#router ospf 10 R2(config-router)#router-id 2.2.2.2 R2(config-router)#end R2# \*Mar 25 20:03:56.863: %SYS-5-CONFIG\_I: Configured from console by console
Enter the show ip protocols command to verify the router ID.
R2#show ip protocols
\*\*\* IP Routing is NSF aware \*\*\*
(output omitted)
Routing Protocol is "ospf 10"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 2.2.2.2
Number of areas in this router is 0. 0 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: (default is 110)
R2#
You are now on R3:
- Enter OSPF router configuration mode using process ID 10
- Assign a router ID of 3.3.3.3
- Return to privileged EXEC mode.
R3(config)#router ospf 10 R3(config-router)#router-id 3.3.3.3 R3(config-router)#end R3# \*Mar 25 20:11:05.415: %SYS-5-CONFIG\_I: Configured from console by console
Enter the show ip protocols command to verify the router ID.
R3#show ip protocols
\*\*\* IP Routing is NSF aware \*\*\*
(output omitted)
Routing Protocol is "ospf 10"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Router ID 3.3.3.3
Number of areas in this router is 0. 0 normal 0 stub 0 nssa
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
Distance: (default is 110)
R3#
You have successfully assigned the router IDs to R2 and R3.
Ready to go! Keep visiting our networking course blog, give Like to our fanpage; and you will find more tools and concepts that will make you a networking professional.