DHCPv6
Summary
This topic explain the operation of DHCPv6. Start learning CCNA 200-301 for free right now!!
Table of Contents
DHCPv6 Operation Steps
This topic explains stateless and stateful DHCPv6. Stateless DHCPv6 uses parts of SLAAC to ensure that all the necessary information is supplied to the host. Stateful DHCPv6 does not require SLAAC.
Although DHCPv6 is similar to DHCPv4 in what it provides, the two protocols are independent of each other.
The host begins the DHCPv6 client/server communications after stateless DHCPv6 or stateful DHCPv6 is indicated in the RA.
Server to client DHCPv6 messages use UDP destination port 546 while client to server DHCPv6 messages use UDP destination port 547.
The steps for DHCPv6 operations are as follows:
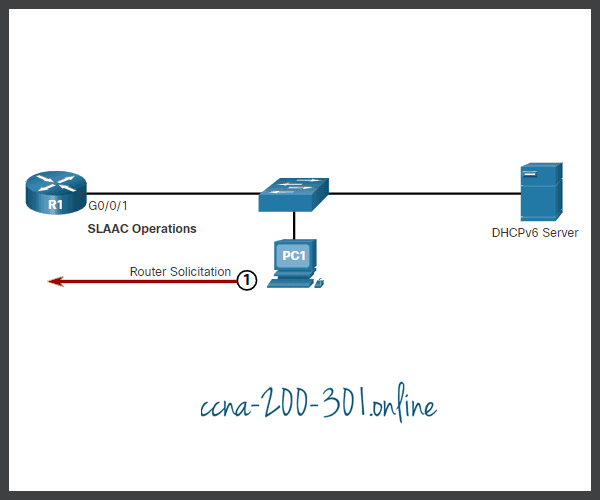
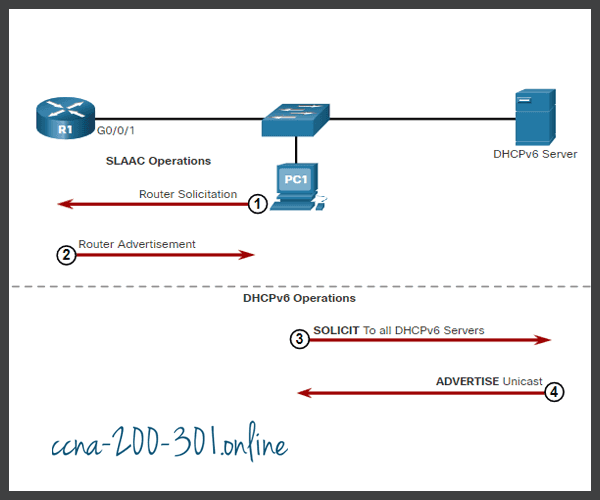
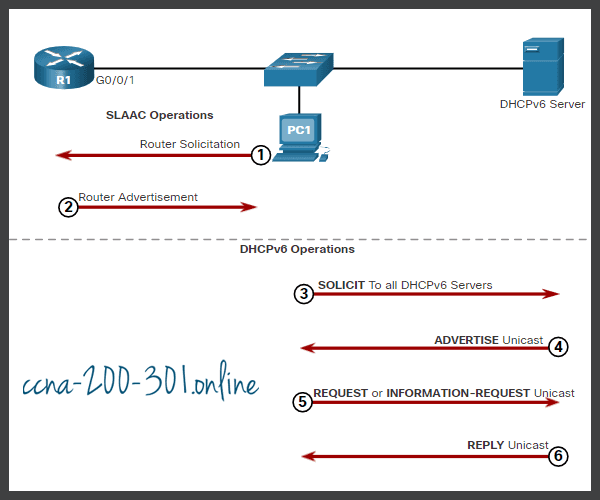
- The host sends an RS message.
- The router responds with an RA message.
- The host sends a DHCPv6 SOLICIT message.
- The DHCPv6 server responds with an ADVERTISE message.
- The host responds to the DHCPv6 server.
- The DHCPv6 server sends a REPLY message.
Click each button for an explanation and illustration of these DHCPv6 operation steps.
Stateless DHCPv6 Operation
The stateless DHCPv6 option tells the client to use the information in the RA message for addressing, but additional configuration parameters are available from a DHCPv6 server.
This process is known as stateless DHCPv6 because the server is not maintaining any client state information (i.e., a list of available and allocated IPv6 addresses). The stateless DHCPv6 server is only providing configuration parameters for clients, not IPv6 addresses.
The figure illustrates stateless DHCPv6 operation.

- PC1 receives a stateless DHCP RA message. The RA message contains the network prefix and prefix length. The M flag for stateful DHCP is set to the default value 0. The A=1 flag tells the client to use SLAAC. The O=1 flag informs the client that additional configuration information is available from a stateless DHCPv6 server.
- The client sends a DHCPv6 SOLICIT message looking for a stateless DHCPv6 server to obtain additional information (e.g., DNS server addresses).
Enable Stateless DHCPv6 on an Interface
Stateless DHCPv6 is enabled on a router interface using the ipv6 nd other-config-flag interface configuration command. This sets the O flag to 1.
The highlighted output confirms the RA will tell receiving hosts to use stateless autoconfigure (A flag = 1) and contact a DHCPv6 server to obtain another configuration information (O flag = 1).
Note: You can use the no ipv6 nd other-config-flag to reset the interface to the default SLAAC only option (O flag = 0).
R1(config-if)# ipv6 nd other-config-flag R1(config-if)# end R1# R1# show ipv6 interface g0/0/1 | begin ND ND DAD is enabled, number of DAD attempts: 1 ND reachable time is 30000 milliseconds (using 30000) ND advertised reachable time is 0 (unspecified) ND advertised retransmit interval is 0 (unspecified) ND router advertisements are sent every 200 seconds ND router advertisements live for 1800 seconds ND advertised default router preference is Medium Hosts use stateless autoconfig for addresses. Hosts use DHCP to obtain other configuration. R1#
Stateful DHCPv6 Operation
This option is most similar to DHCPv4. In this case, the RA message tells the client to obtain all addressing information from a stateful DHCPv6 server, except the default gateway address which is the source IPv6 link-local address of the RA.
This is known as stateful DHCPv6 because the DHCPv6 server maintains IPv6 state information. This is similar to a DHCPv4 server allocating addresses for IPv4.
The figure illustrates stateful DHCPv6 operation.
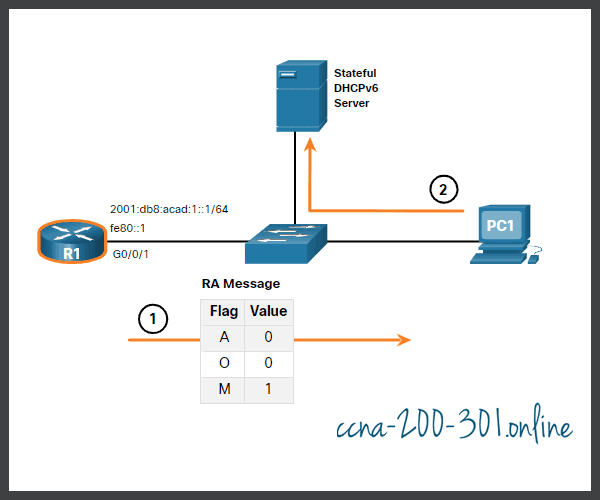
- PC1 receives a DHCPv6 RA message with the O flag set to 0 and the M flag set to 1, indicating to PC1 that it will receive all its IPv6 addressing information from a stateful DHCPv6 server.
- PC1 sends a DHCPv6 SOLICIT message looking for a stateful DHCPv6 server.
Enable Stateful DHCPv6 on an Interface
Stateful DHCPv6 is enabled on a router interface using the ipv6 nd managed-config-flag interface configuration command. This sets the M flag to 1.
The highlighted output in the example confirms that the RA will tell the host to obtain all IPv6 configuration information from a DHCPv6 server (M flag = 1).
R1(config)# int g0/0/1 R1(config-if)# ipv6 nd managed-config-flag R1(config-if)# end R1# R1# show ipv6 interface g0/0/1 | begin ND ND DAD is enabled, number of DAD attempts: 1 ND reachable time is 30000 milliseconds (using 30000) ND advertised reachable time is 0 (unspecified) ND advertised retransmit interval is 0 (unspecified) ND router advertisements are sent every 200 seconds ND router advertisements live for 1800 seconds ND advertised default router preference is Medium Hosts use DHCP to obtain routable addresses. R1#
Ready to go! Keep visiting our networking course blog, give Like to our fanpage; and you will find more tools and concepts that will make you a networking professional.