DHCPv4 Concepts
Summary
This topic explain how DHCPv4 operates in a small- to medium-sized business network. Start learning CCNA 200-301 for free right now!!
Table of Contents
DHCPv4 Server and Client
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol v4 (DHCPv4) assigns IPv4 addresses and other network configuration information dynamically. Because desktop clients typically make up the bulk of network nodes, DHCPv4 is an extremely useful and timesaving tool for network administrators.
A dedicated DHCPv4 server is scalable and relatively easy to manage. However, in a small branch or SOHO location, a Cisco router can be configured to provide DHCPv4 services without the need for a dedicated server. Cisco IOS software supports an optional, full-featured DHCPv4 server.
The DHCPv4 server dynamically assigns, or leases, an IPv4 address from a pool of addresses for a limited period of time chosen by the server, or until the client no longer needs the address.
Clients lease the information from the server for an administratively defined period. Administrators configure DHCPv4 servers to set the leases to time out at different intervals. The lease is typically anywhere from 24 hours to a week or more. When the lease expires, the client must ask for another address, although the client is typically reassigned the same address.

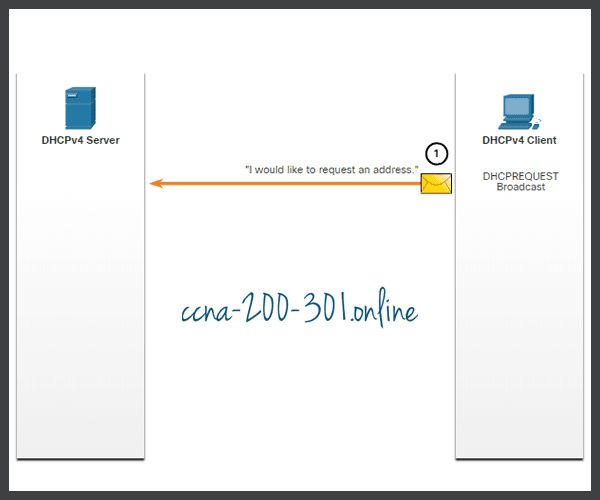
- The DHCPv4 lease process begins with the client sending a message requesting the services of a DHCP server.
- If there is a DHCPv4 server that receives the message, it will respond with an IPv4 address and possible other network configuration information.
DHCPv4 Operation
DHCPv4 works in a client/server mode. When a client communicates with a DHCPv4 server, the server assigns or leases an IPv4 address to that client. The client connects to the network with that leased IPv4 address until the lease expires. The client must contact the DHCP server periodically to extend the lease. This lease mechanism ensures that clients that move or power off do not keep addresses that they no longer need. When a lease expires, the DHCP server returns the address to the pool where it can be reallocated as necessary.
Steps to Obtain a Lease
When the client boots (or otherwise wants to join a network), it begins a four-step process to obtain a lease:
- DHCP Discover (DHCPDISCOVER)
- DHCP Offer (DHCPOFFER)
- DHCP Request (DHCPREQUEST)
- DHCP Acknowledgment (DHCPACK)
Click each button to learn the four-step process to obtain a DHCP lease.
Steps to Renew a Lease
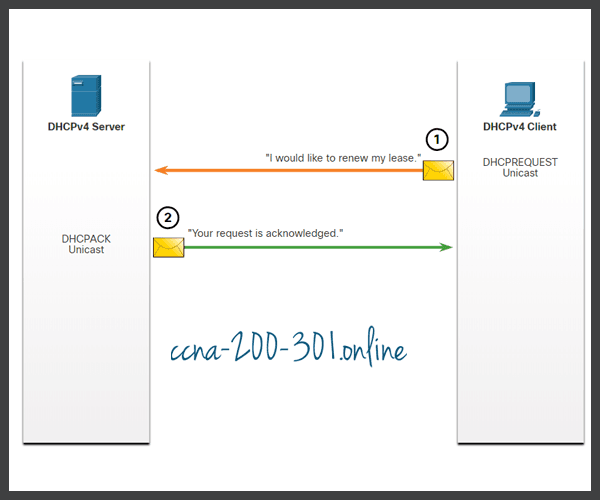
Prior to lease expiration, the client begins a two-step process to renew the lease with the DHCPv4 server, as shown in the figure:
1. DHCP Request (DHCPREQUEST)
Before the lease expires, the client sends a DHCPREQUEST message directly to the DHCPv4 server that originally offered the IPv4 address. If a DHCPACK is not received within a specified amount of time, the client broadcasts another DHCPREQUEST so that one of the other DHCPv4 servers can extend the lease.
2. DHCP Acknowledgment (DHCPACK)
On receiving the DHCPREQUEST message, the server verifies the lease information by returning a DHCPACK.
Ready to go! Keep visiting our networking course blog, give Like to our fanpage; and you will find more tools and concepts that will make you a networking professional.