Device Discovery with CDP
Summary
This topic use CDP to map a network topology. Start learning CCNA 200-301 for free right now!!
Table of Contents
CDP Overview
The first thing you want to know about your network is what is in it? Where are these components? How are they connected? Basically, you need a map. This topic explains how you can use Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) to create a map of your network.
CDP is a Cisco proprietary Layer 2 protocol that is used to gather information about Cisco devices which share the same data link. CDP is media and protocol independent and runs on all Cisco devices, such as routers, switches, and access servers.
The device sends periodic CDP advertisements to connected devices, as shown in the figure.
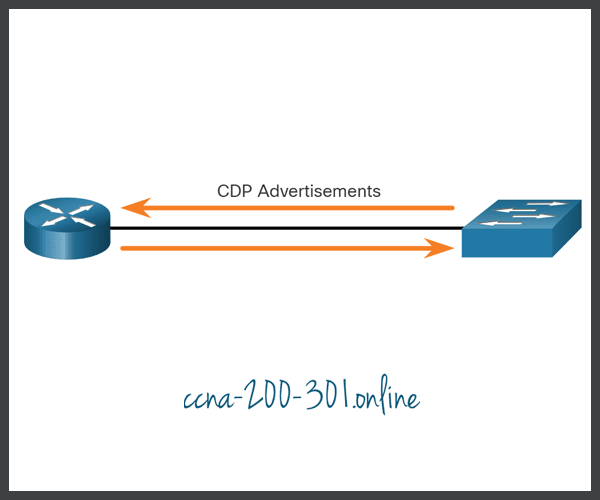
These advertisements share information about the type of device that is discovered, the name of the devices, and the number and type of the interfaces.
Because most network devices are connected to other devices, CDP can assist in network design decisions, troubleshooting, and making changes to equipment. CDP can also be used as a network discovery tool to determine the information about the neighboring devices. This information gathered from CDP can help build a logical topology of a network when documentation is missing or lacking in detail.
Configure and Verify CDP
For Cisco devices, CDP is enabled by default. For security reasons, it may be desirable to disable CDP on a network device globally, or per interface. With CDP, an attacker can gather valuable insight about the network layout, such as IP addresses, IOS versions, and types of devices.
To verify the status of CDP and display information about CDP, enter the show cdp command, as displayed in the example.
Router# show cdp
Global CDP information:
Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds
Sending a holdtime value of 180 seconds
Sending CDPv2 advertisements is enabled
To enable CDP globally for all the supported interfaces on the device, enter cdp run in the global configuration mode. CDP can be disabled for all the interfaces on the device with the no cdp run command in the global configuration mode.
Router(config)# no cdp run Router(config)# exit Router# show cdp CDP is not enabled Router# configure terminal Router(config)# cdp run
To disable CDP on a specific interface, such as the interface facing an ISP, enter no cdp enable in the interface configuration mode. CDP is still enabled on the device; however, no more CDP advertisements will be sent out that interface. To enable CDP on the specific interface again, enter cdp enable, as shown in the example.
Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/0/1 Switch(config-if)# cdp enable
To verify the status of CDP and display a list of neighbors, use the show cdp neighbors command in the privileged EXEC mode. The show cdp neighbors command displays important information about the CDP neighbors. Currently, this device does not have any neighbors because it is not physically connected to any devices, as indicated by the results of the show cdp neighbors command displayed in the example.
Router# show cdp neighbors
Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans Bridge, B - Source Route Bridge
S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, P - Phone,
D - Remote, C - CVTA, M - Two-port Mac Relay
Device ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port ID
Total cdp entries displayed : 0
Use the show cdp interface command to display the interfaces that are CDP-enabled on a device. The status of each interface is also displayed. The figure shows that five interfaces are CDP-enabled on the router with only one active connection to another device.
Router# show cdp interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0 is administratively down, line protocol is down Encapsulation ARPA Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds GigabitEthernet0/0/1 is up, line protocol is up Encapsulation ARPA Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds GigabitEthernet0/0/2 is down, line protocol is down Encapsulation ARPA Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds Serial0/1/0 is administratively down, line protocol is down Encapsulation HDLC Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds Serial0/1/1 is administratively down, line protocol is down Encapsulation HDLC Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds GigabitEthernet0 is down, line protocol is down Encapsulation ARPA Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds cdp enabled interfaces : 6 interfaces up : 1 interfaces down : 5
Discover Devices by Using CDP
Consider the lack of documentation in the topology shown in the figure. The network administrator only knows that R1 is connected to another device.

With CDP enabled on the network, the show cdp neighbors command can be used to determine the network layout, as shown in the output.
R1# show cdp neighbors
Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans Bridge, B - Source Route Bridge
S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, P - Phone,
D - Remote, C - CVTA, M - Two-port Mac Relay
Device ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port ID
S1 Gig 0/0/1 179 S I WS-C3560- Fas 0/5
No information is available regarding the rest of the network. The show cdp neighbors command provides helpful information about each CDP neighbor device, including the following:
- Device identifiers – This is the host name of the neighbor device (S1).
- Port identifier – This is the name of the local and remote port (G0/0/1 and F0/5, respectively).
- Capabilities list – This shows whether the device is a router or a switch (S for switch; I for IGMP is beyond scope for this course)
- Platform – This is the hardware platform of the device (WS-C3560 for Cisco 3560 switch).
The output shows that there is another Cisco device, S1, connected to the G0/0/1 interface on R1. Furthermore, S1 is connected through its F0/5, as shown in the updated topology.

The network administrator uses show cdp neighbors detail to discover the IP address for S1. As displayed in the output, the address for S1 is 192.168.1.2.
R1# show cdp neighbors detail ------------------------- Device ID: S1 Entry address(es): IP address: 192.168.1.2 Platform: cisco WS-C3560-24TS, Capabilities: Switch IGMP Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/1, Port ID (outgoing port): FastEthernet0/5 Holdtime : 136 sec Version : Cisco IOS Software, C3560 Software (C3560-LANBASEK9-M), Version 15.0(2)SE7, R RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1) Technical Support: http://www.cisco.com/techsupport Copyright (c) 1986-2014 by Cisco Systems, Inc. Compiled Thu 23-Oct-14 14:49 by prod_rel_team advertisement version: 2 Protocol Hello: OUI=0x00000C, Protocol ID=0x0112; payload len=27, value=00000000FFFFFFFF010221FF000000000000002291210380FF0000 VTP Management Domain: '' Native VLAN: 1 Duplex: full Management address(es): IP address: 192.168.1.2 Total cdp entries displayed : 1
By accessing S1 either remotely through SSH, or physically through the console port, the network administrator can determine what other devices are connected to S1, as displayed in the output of the show cdp neighbors in the figure.
S1# show cdp neighbors
Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans Bridge, B - Source Route Bridge
S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, P - Phone,
D - Remote, C - CVTA, M - Two-port Mac Relay
Device ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port ID
S2 Fas 0/1 150 S I WS-C2960- Fas 0/1
R1 Fas 0/5 179 R S I ISR4331/K Gig 0/0/1
Another switch, S2, is revealed in the output. S2 is using F0/1 to connect to the F0/1 interface on S1, as shown in the figure.
Again, the network administrator can use show cdp neighbors detail to discover the IP address for S2, and then remotely access it. After a successful login, the network administrator uses the show cdp neighbors command to discover if there are more devices.
S2# show cdp neighbors
Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans Bridge, B - Source Route Bridge
S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, P - Phone,
D - Remote, C - CVTA, M - Two-port Mac Relay
Device ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port ID
S1 Fas 0/1 141 S I WS-C3560- Fas 0/1
The only device connected to S2 is S1. Therefore, there are no more devices to discover in the topology. The network administrator can now update the documentation to reflect the discovered devices.
Syntax Checker – Configure and Verify CDP
Practice configuring and verifying CDP.
Display the status of CDP on R1.
R1#show cdp % CDP is not enabled
Enter Global Configuration mode to configure the following:
- Enable CDP globally on R1.
- Disable CDP on interface S0/0/0. Use s0/0/0 as the interface designation.
- Use end command to exit Global Configuration mode.
R1#configure terminal R1(config)#cdp run R1(config)#interface s0/0/0 R1(config-if)#no cdp enable R1(config-if)#end *Oct 2 15:43:46.288: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Display the list of CDP neighbors on R1.
R1#show cdp neighbors
Capability Codes: R - Router, T - Trans Bridge, B - Source Route Bridge
S - Switch, H - Host, I - IGMP, r - Repeater, P - Phone,
D - Remote, C - CVTA, M - Two-port Mac Relay
Device ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port ID
S1 Gig 0/0/1 179 S I WS-C3560- Fas 0/5
Display more details from the list of CDP neighbors on R1.
R1#show cdp neighbors detail
\-------------------------
Device ID: S1
Entry address(es):
Platform: cisco WS-C3560-24TS, Capabilities: Switch IGMP
Interface: GigabitEthernet0/0/1, Port ID (outgoing port): FastEthernet0/5
Holdtime : 174 sec
Version :
Cisco IOS Software, C3560 Software (C3560-IPSERVICESK9-M), Version 15.0(2)SE7, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1)
Technical Support: http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Copyright (c) 1986-2014 by Cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Thu 23-Oct-14 14:13 by prod_rel_team
advertisement version: 2
Protocol Hello: OUI=0x00000C, Protocol ID=0x0112; payload len=27, value=00000000FFFFFFFF010221FF000000000000FCFBFB957300FF0000
VTP Management Domain: ''
Native VLAN: 1
Duplex: full
Total cdp entries displayed : 1
You have successfully configured and verified CDP on the router.
Packet Tracer – Use CDP to Map a Network
A senior network administrator requires you to map the Remote Branch Office network and discover the name of a recently installed switch that still needs an IPv4 address to be configured. Your task is to create a map of the branch office network. To map the network, you will use SSH for remote access and the Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) to discover information about neighboring network devices, like routers and switches.
Ready to go! Keep visiting our networking course blog, give Like to our fanpage; and you will find more tools and concepts that will make you a networking professional.






