Configure a Switch with Initial Settings
Summary
This topic is for configure initial settings on a Cisco switch. Start learning CCNA 200-301 for free right now!!
Table of Contents
Switch Boot Sequence
Before you can configure a switch, you need to turn it on and allow it to go through the five-step boot sequence. This topic covers the basics of configuring a switch and includes a lab at the end.
After a Cisco switch is powered on, it goes through the following five-step boot sequence:
- Step 1: First, the switch loads a power-on self-test (POST) program stored in ROM. POST checks the CPU subsystem. It tests the CPU, DRAM, and the portion of the flash device that makes up the flash file system.
- Step 2: Next, the switch loads the boot loader software. The boot loader is a small program stored in ROM that is run immediately after POST successfully completes.
- Step 3: The boot loader performs low-level CPU initialization. It initializes the CPU registers, which control where physical memory is mapped, the quantity of memory, and its speed.
- Step 4: The boot loader initializes the flash file system on the system board.
- Step 5: Finally, the boot loader locates and loads a default IOS operating system software image into memory and gives control of the switch over to the IOS.
The boot system Command
The switch attempts to automatically boot by using information in the BOOT environment variable. If this variable is not set, the switch attempts to load and execute the first executable file it can find. On Catalyst 2960 Series switches, the image file is normally contained in a directory that has the same name as the image file (excluding the .bin file extension).
The IOS operating system then initializes the interfaces using the Cisco IOS commands found in the startup-config file. The startup-config file is called config.text and is located in flash.
In the example, the BOOT environment variable is set using the boot system global configuration mode command. Notice that the IOS is located in a distinct folder and the folder path is specified. Use the command show boot to see what the current IOS boot file is set to.
S1(config)# boot system flash:/c2960-lanbasek9-mz.150-2.SE/c2960-lanbasek9-mz.150-2.SE.bin
The table defines each part of the boot system command.
| Command | Definition |
|---|---|
boot system |
The main command |
flash: |
The storage device |
c2960-lanbasek9-mz.150-2.SE/ |
The path to the file system |
c2960-lanbasek9-mz.150-2.SE.bin |
The IOS file name |
Switch LED Indicators
Cisco Catalyst switches have several status LED indicator lights. You can use the switch LEDs to quickly monitor switch activity and performance. Switches of different models and feature sets will have different LEDs and their placement on the front panel of the switch may also vary.
The figure shows the switch LEDs and the Mode button for a Cisco Catalyst 2960 switch.
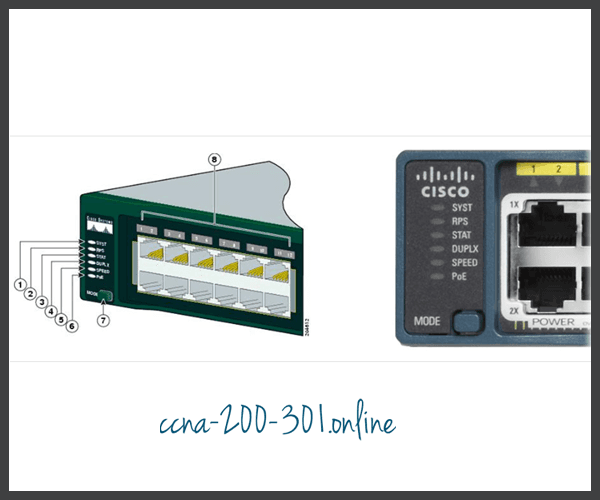
The Mode button (7 in the figure) is used to toggle through port status, port duplex, port speed, and if supported, the Power over Ethernet (PoE) status of the port LEDs (8 in the figure).
Click each button to learn the purpose of the LED indicators (1-6 in the figure), and the meaning of their colors:
Recovering from a System Crash
The boot loader provides access into the switch if the operating system cannot be used because of missing or damaged system files. The boot loader has a command-line that provides access to the files stored in flash memory.
The boot loader can be accessed through a console connection following these steps:
Step 1. Connect a PC by console cable to the switch console port. Configure terminal emulation software to connect to the switch.
Step 2. Unplug the switch power cord.
Step 3. Reconnect the power cord to the switch and, within 15 seconds, press and hold down the Mode button while the System LED is still flashing green.
Step 4. Continue pressing the Mode button until the System LED turns briefly amber and then solid green; then release the Mode button.
Step 5. The boot loader switch: prompt appears in the terminal emulation software on the PC.
Type the help or ? at the boot loader prompt to view a list of available commands.
By default, the switch attempts to automatically boot up by using information in the BOOT environment variable. To view the path of the switch BOOT environment variable type the set command. Then, initialize the flash file system using the flash_init command to view the current files in flash, as shown in the output.
switch: set BOOT=flash:/c2960-lanbasek9-mz.122-55.SE7/c2960-lanbasek9-mz.122-55.SE7.bin (output omitted) switch: flash_init Initializing Flash... flashfs[0]: 2 files, 1 directories flashfs[0]: 0 orphaned files, 0 orphaned directories flashfs[0]: Total bytes: 32514048 flashfs[0]: Bytes used: 11838464 flashfs[0]: Bytes available: 20675584 flashfs[0]: flashfs fsck took 10 seconds. ...done Initializing Flash.
After flash has finished initializing you can enter the dir flash: command to view the directories and files in flash, as shown in the output.
switch: dir flash: Directory of flash:/ 2 -rwx 11834846 c2960-lanbasek9-mz.150-2.SE8.bin 3 -rwx 2072 multiple-fs
Enter the BOOT=flash command to change the BOOT environment variable path the switch uses to load the new IOS in flash. To verify the new BOOT environment variable path, issue the set command again. Finally, to load the new IOS type the boot command without any arguments, as shown in the output.
switch: BOOT=flash:c2960-lanbasek9-mz.150-2.SE8.bin switch: set BOOT=flash:c2960-lanbasek9-mz.150-2.SE8.bin (output omitted) switch: boot
The boot loader commands support initializing flash, formatting flash, installing a new IOS, changing the BOOT environment variable and recovery of lost or forgotten passwords.
Switch Management Access
To prepare a switch for remote management access, the switch must be configured with an IP address and a subnet mask. Keep in mind that to manage the switch from a remote network, the switch must be configured with a default gateway. This is very similar to configuring the IP address information on host devices. In the figure, the switch virtual interface (SVI) on S1 should be assigned an IP address. The SVI is a virtual interface, not a physical port on the switch. A console cable is used to connect to a PC so that the switch can be initially configured.

Switch SVI Configuration Example
By default, the switch is configured to have its management controlled through VLAN 1. All ports are assigned to VLAN 1 by default. For security purposes, it is considered a best practice to use a VLAN other than VLAN 1 for the management VLAN, such as VLAN 99 in the example.
Ready to go! Keep visiting our networking course blog, give Like to our fanpage; and you will find more tools and concepts that will make you a networking professional.





