ICMP Messages
Summary
This topic explain how ICMP is used to test network connectivity.. Start learning CCNA 200-301 for free right now!!
Table of Contents
ICMPv4 and ICMPv6 Messages
In this topic, you will learn about the different types of Internet Control Message Protocols (ICMPs), and the tools that are used to send them.
Although IP is only a best-effort protocol, the TCP/IP suite does provide for error messages and informational messages when communicating with another IP device. These messages are sent using the services of ICMP. The purpose of these messages is to provide feedback about issues related to the processing of IP packets under certain conditions, not to make IP reliable. ICMP messages are not required and are often not allowed within a network for security reasons.
ICMP is available for both IPv4 and IPv6. ICMPv4 is the messaging protocol for IPv4. ICMPv6 provides these same services for IPv6 but includes additional functionality. In this course, the term ICMP will be used when referring to both ICMPv4 and ICMPv6.
The types of ICMP messages, and the reasons why they are sent, are extensive. The ICMP messages common to both ICMPv4 and ICMPv6 and discussed in this module include:
- Host reachability
- Destination or Service Unreachable
- Time exceeded
Host Reachability
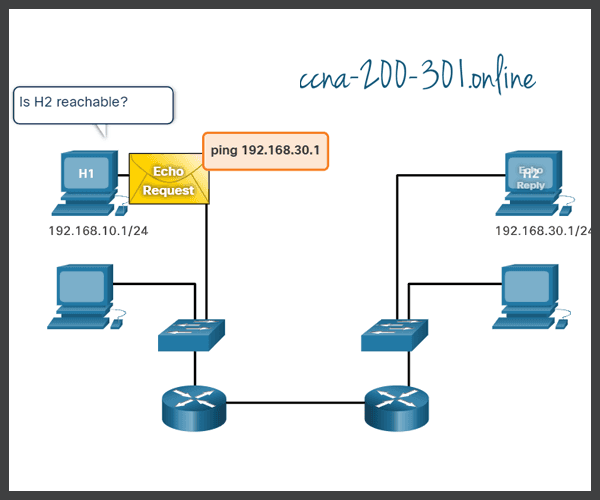
An ICMP Echo Message can be used to test the reachability of a host on an IP network. The local host sends an ICMP Echo Request to a host. If the host is available, the destination host responds with an Echo Reply. In the figure, click the Play button to see an animation of the ICMP Echo Request/Echo Reply. This use of the ICMP Echo messages is the basis of the ping utility.
Destination or Service Unreachable
When a host or gateway receives a packet that it cannot deliver, it can use an ICMP Destination Unreachable message to notify the source that the destination or service is unreachable. The message will include a code that indicates why the packet could not be delivered.
Some of the Destination Unreachable codes for ICMPv4 are as follows:
- 0 – Net unreachable
- 1 – Host unreachable
- 2 – Protocol unreachable
- 3 – Port unreachable
Some of the Destination Unreachable codes for ICMPv6 are as follows:
- 0 – No route to destination
- 1 – Communication with the destination is administratively prohibited (e.g., firewall)
- 2 – Beyond scope of the source address
- 3 – Address unreachable
- 4 – Port unreachable
Time Exceeded
An ICMPv4 Time Exceeded message is used by a router to indicate that a packet cannot be forwarded because the Time to Live (TTL) field of the packet was decremented to 0. If a router receives a packet and decrements the TTL field in the IPv4 packet to zero, it discards the packet and sends a Time Exceeded message to the source host.
ICMPv6 also sends a Time Exceeded message if the router cannot forward an IPv6 packet because the packet has expired. Instead of the IPv4 TTL field, ICMPv6 uses the IPv6 Hop Limit field to determine if the packet has expired.
ICMPv6 Messages
The informational and error messages found in ICMPv6 are very similar to the control and error messages implemented by ICMPv4. However, ICMPv6 has new features and improved functionality not found in ICMPv4. ICMPv6 messages are encapsulated in IPv6.
ICMPv6 includes four new protocols as part of the Neighbor Discovery Protocol (ND or NDP).
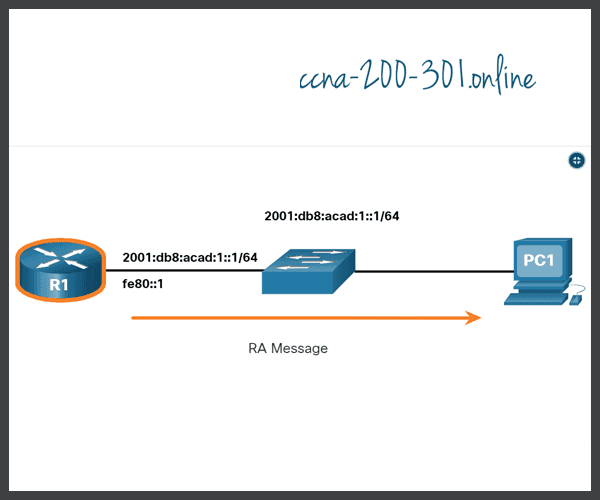
Messaging between an IPv6 router and an IPv6 device, including dynamic address allocation are as follows:
- Router Solicitation (RS) message
- Router Advertisement (RA) message
Messaging between IPv6 devices, including duplicate address detection and address resolution are as follows:
- Neighbor Solicitation (NS) message
- Neighbor Advertisement (NA) message
Ready to go! Keep visiting our networking course blog, give Like to our fanpage; and you will find more tools and concepts that will make you a networking professional.