Hexadecimal Number System
Summary
This topic calculate numbers between decimal and hexadecimal systems. Start learning CCNA 200-301 for free right now!!
Table of Contents
Hexadecimal and IPv6 Addresses
Now you know how to convert binary to decimal and decimal to binary. You need that skill to understand IPv4 addressing in your network. But you are just as likely to be using IPv6 addresses in your network. To understand IPv6 addresses, you must be able to convert hexadecimal to decimal and vice versa.
Just as decimal is a base ten number system, hexadecimal is a base sixteen system. The base sixteen number system uses the digits 0 to 9 and the letters A to F. The figure shows the equivalent decimal and hexadecimal values for binary 0000 to 1111.
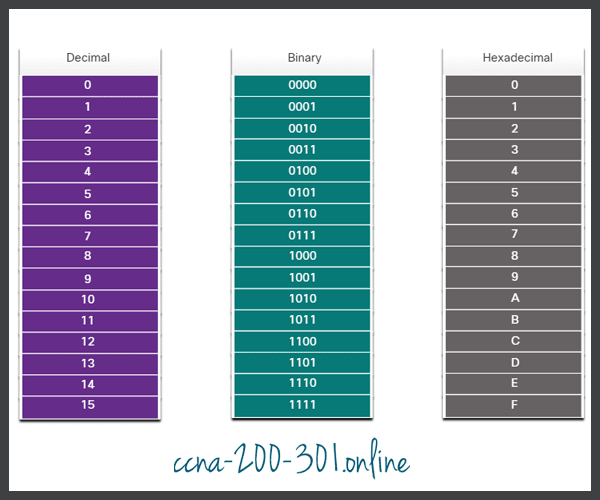
Binary and hexadecimal work well together because it is easier to express a value as a single hexadecimal digit than as four binary bits.
The hexadecimal numbering system is used in networking to represent IP Version 6 addresses and Ethernet MAC addresses.
IPv6 addresses are 128 bits in length and every 4 bits is represented by a single hexadecimal digit; for a total of 32 hexadecimal values. IPv6 addresses are not case-sensitive and can be written in either lowercase or uppercase.
As shown in the figure, the preferred format for writing an IPv6 address is x:x:x:x:x:x:x:x, with each “x” consisting of four hexadecimal values. When referring to 8 bits of an IPv4 address we use the term octet. In IPv6, a hextet is the unofficial term used to refer to a segment of 16 bits or four hexadecimal values. Each “x” is a single hextet, 16 bits, or four hexadecimal digits.

The sample topology in the figure displays IPv6 hexadecimal addresses.

Video – Converting Between Hexadecimal and Decimal Numbering Systems
Click Play in the video to see how to convert between hexadecimal and decimal numbering systems.
Decimal to Hexadecimal Conversions
Converting decimal numbers to hexadecimal values is straightforward. Follow the steps listed:
- Convert the decimal number to 8-bit binary strings.
- Divide the binary strings in groups of four starting from the rightmost position.
- Convert each four binary numbers into their equivalent hexadecimal digit.
The example provides the steps for converting 168 to hexadecimal.
For example, 168 converted into hex using the three-step process.
- 168 in binary is 10101000.
- 10101000 in two groups of four binary digits is 1010 and 1000.
- 1010 is hex A and 1000 is hex 8.
Answer: 168 is A8 in hexadecimal.
Hexadecimal to Decimal Conversion
Converting hexadecimal numbers to decimal values is also straightforward. Follow the steps listed:
- Convert the hexadecimal number to 4-bit binary strings.
- Create 8-bit binary grouping starting from the rightmost position.
- Convert each 8-bit binary grouping into their equivalent decimal digit.
This example provides the steps for converting D2 to decimal.
- D2 in 4-bit binary strings is 1101 and 0010.
- 1101 and 0010 is 11010010 in an 8-bit grouping.
- 11010010 in binary is equivalent to 210 in decimal.
Answer: D2 in hexadecimal is 210 in decimal.
Ready to go! Keep visiting our networking course blog, give Like to our fanpage; and you will find more tools and concepts that will make you a networking professional.





